PA Placements e-learning 2025
Section outline
-
Essential Information
Welcome to the "Understanding and Supporting Physician Associate Students in Clinical Placements" e-learning program! This comprehensive training module is designed to equip you with the knowledge and skills necessary to effectively support Physician Associate (PA) students during their clinical placements. By engaging with this program, you will gain a deeper understanding of the PA role, educational structure, and the essential components of a successful clinical placement experience.
Hint: to open or close all topic areas clicking on expand/collapse topics on the top right. -
Below is an overview of the modules included in this program:
Module 1: Introduction to Physician Associates (PAs)
Gain a comprehensive understanding of the role, responsibilities, and key competencies of Physician Associates.
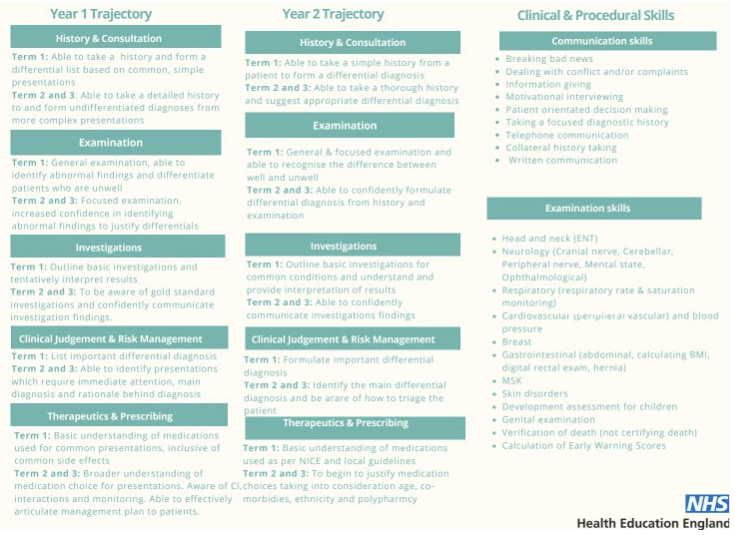
Module 2: Structure of Teaching and Learning for PA Students
Explore the curriculum and training structure for PA students.
Module 3: Learning Opportunities on Placement
Identify suitable learning activities and opportunities for PA students during their placements.
Module 4: Supporting PA Students and Newly Graduated PAs
Learn about mentoring and supervision guidelines tailored to the unique needs of PA students.
Module 5: Integration with Other Healthcare Students and the Multidisciplinary Team (MDT)
Understand the importance of interprofessional collaboration and teamwork.
Module 6: Assessment and Feedback for PA Students
Get an overview of assessment methods for evaluating PA students' competencies.
Module 7: Compliance and Quality Assurance
Ensure compliance with GMC and FPA standards.
Module 8: Conclusion and Resources
Review the key points covered throughout the program.
By the end of this program, you will be well-equipped to support PA students effectively, ensuring they have a positive and enriching clinical placement experience. Thank you for your commitment to fostering the next generation of healthcare professionals.
Let's get started!
-
How to Use This Program:
Navigation:
- The program is divided into eight modules, each focusing on a specific aspect of PA student placements. You can navigate through the modules sequentially or select specific modules based on your needs and interests.
Interactive Elements:
- Engage with interactive elements such as quizzes, case studies, and practical scenarios to reinforce your learning and apply concepts to real-world situations.
Resources and Tools:
- Access additional resources and tools provided within each module to deepen your understanding and support your role as a placement provider.
Assessment and Feedback:
- Complete quizzes and assessments to test your knowledge and receive feedback on your progress. Use these opportunities to reflect on your learning and identify areas for improvement.
Continuous Improvement:
- We encourage you to provide feedback on this e-learning program. Your insights and experiences are valuable in helping us refine and enhance the training for future users.